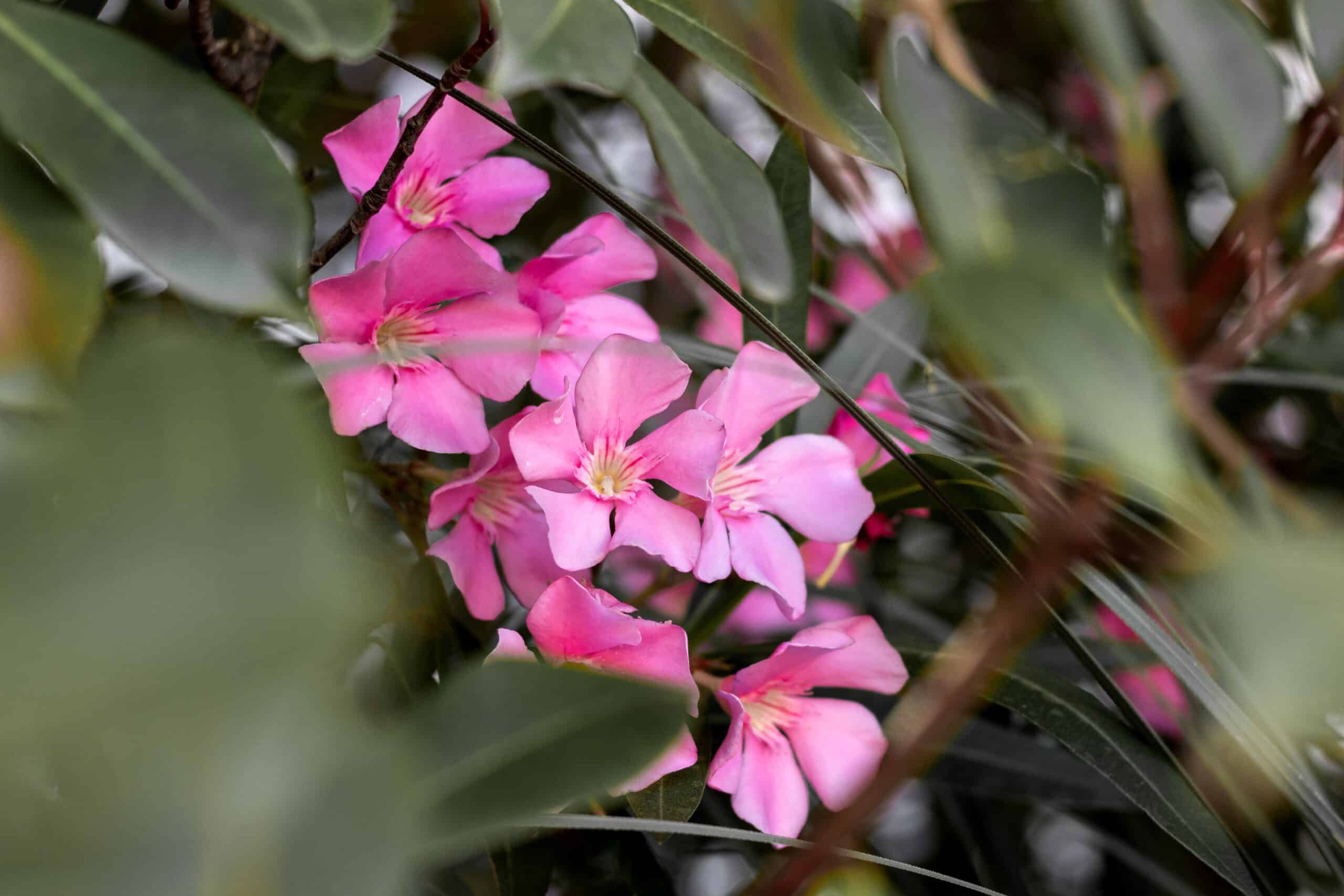
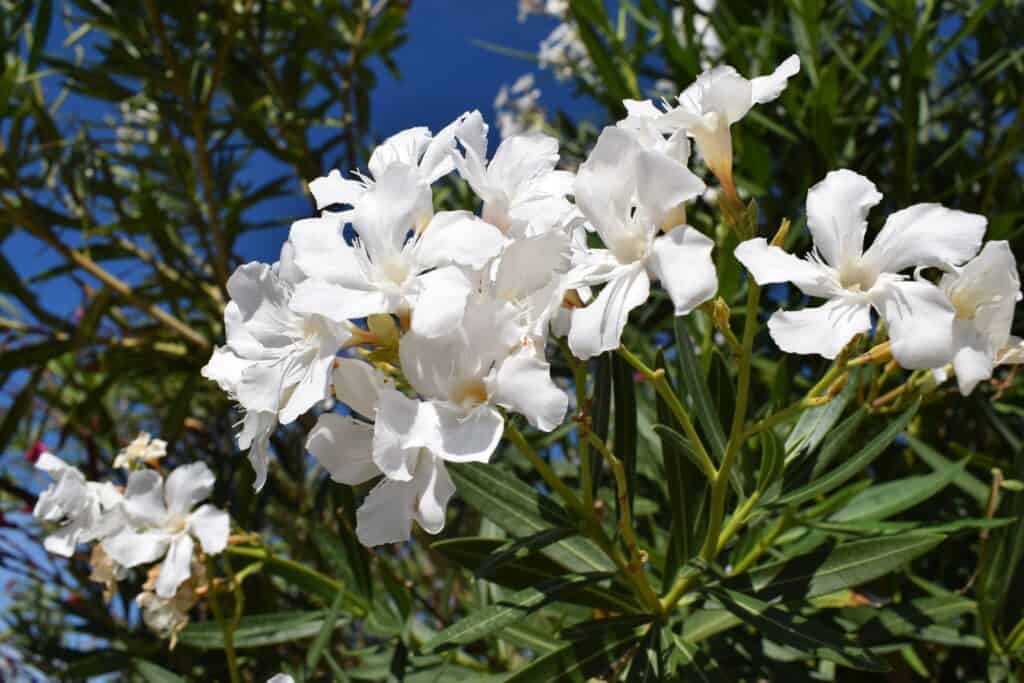
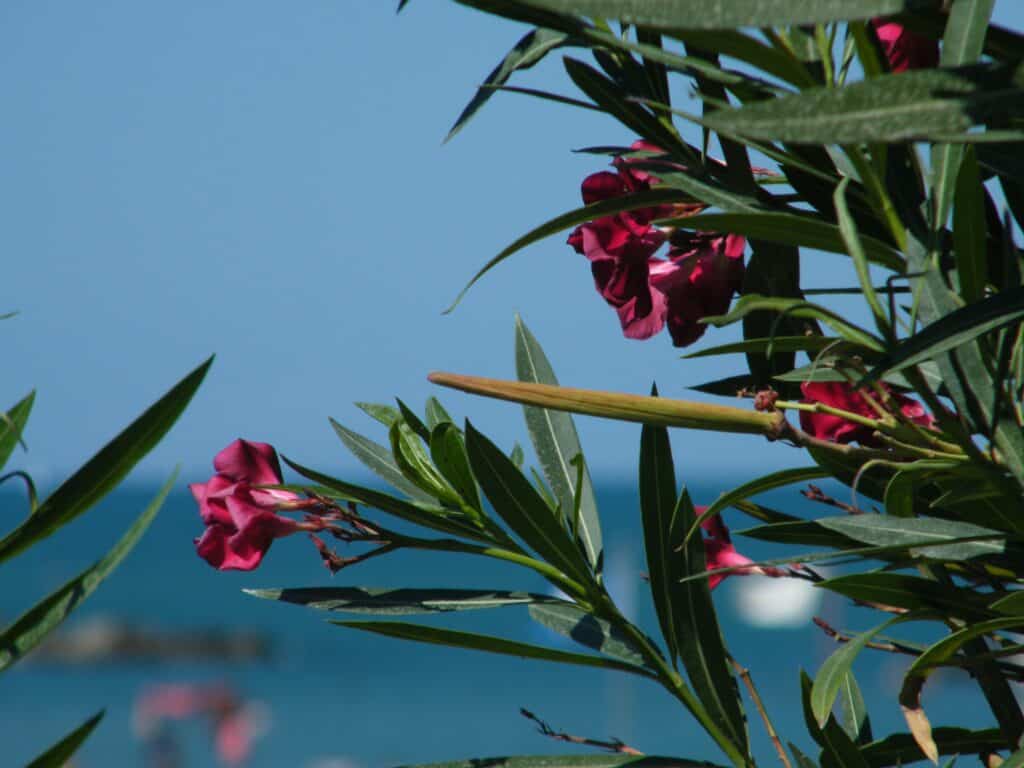
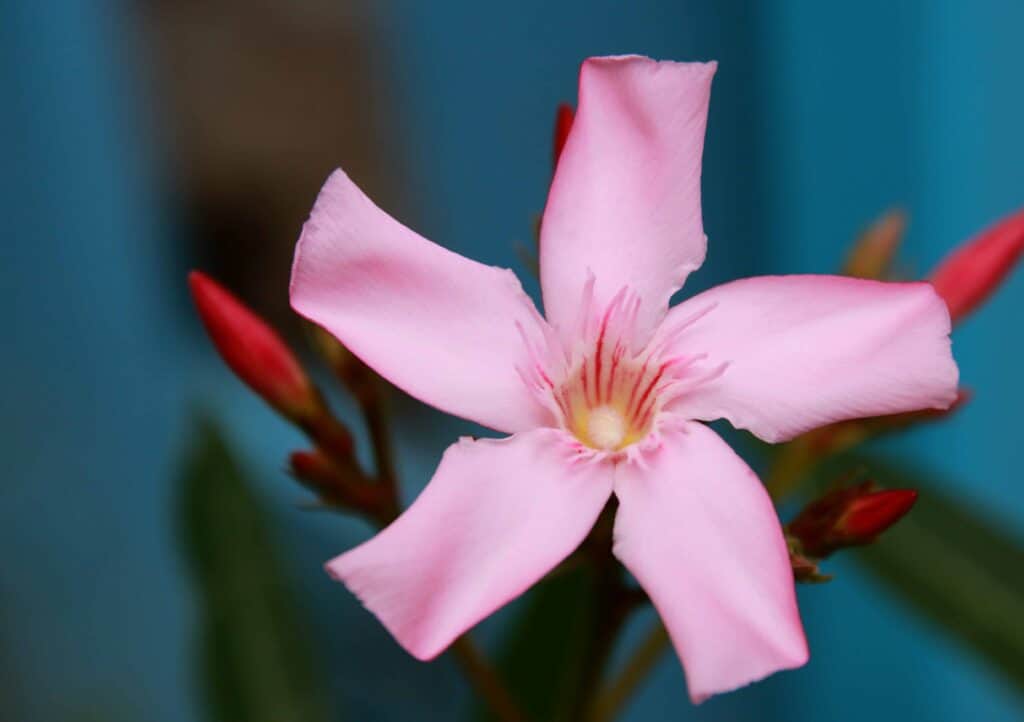
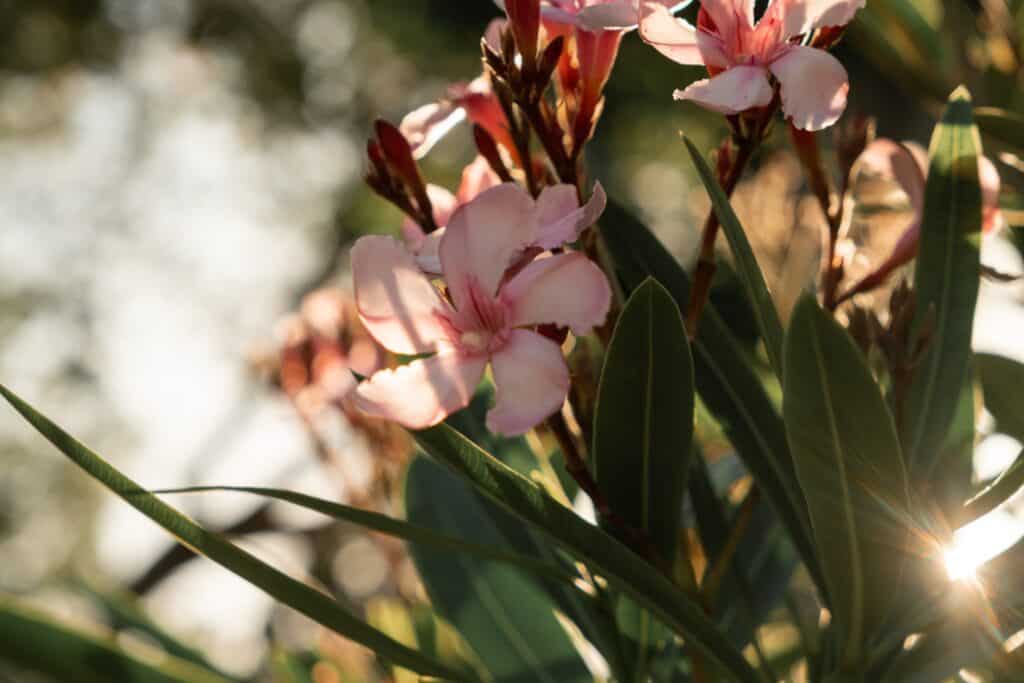
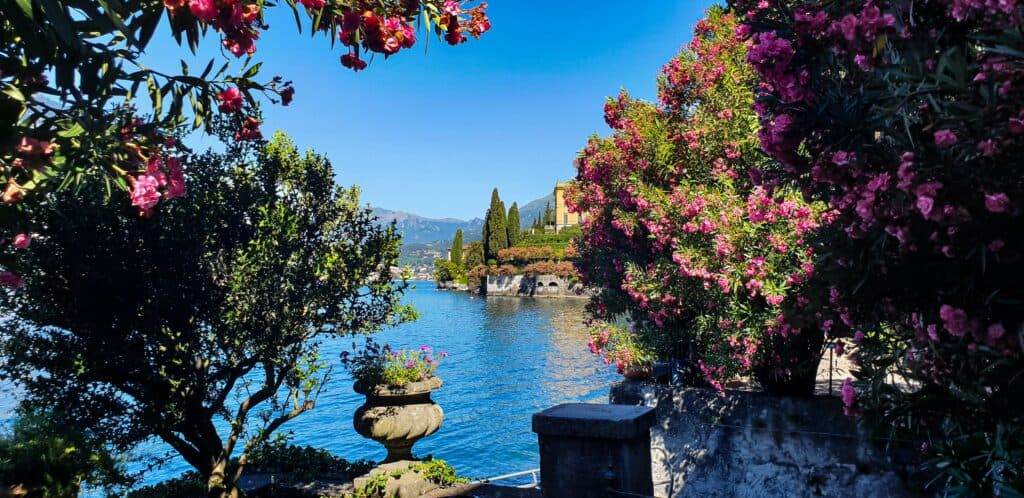
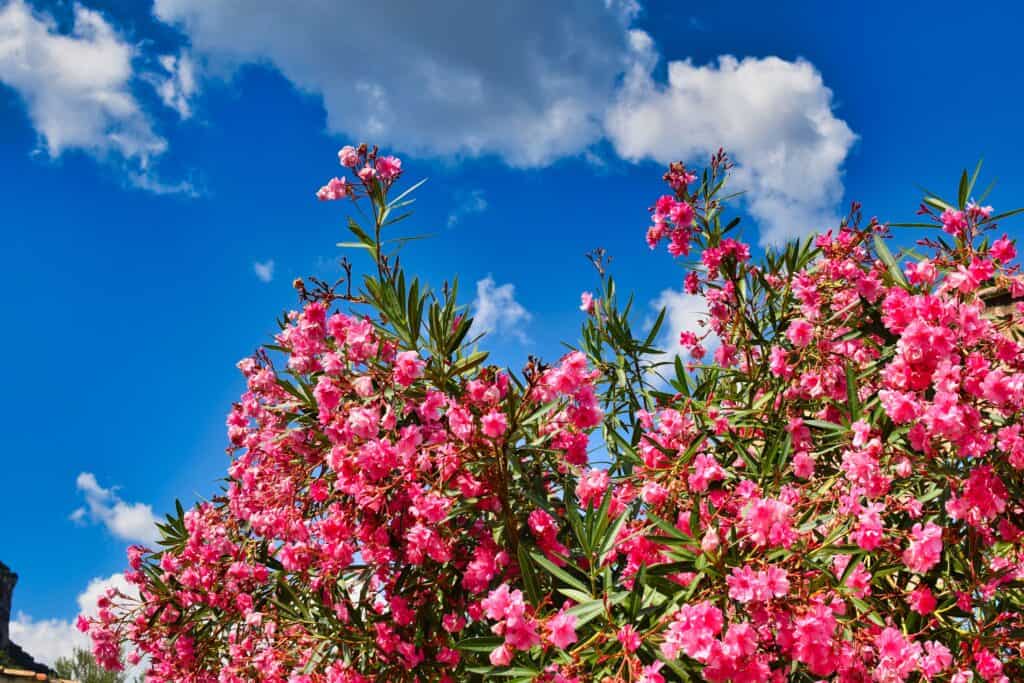
Oleander is a flowering shrub or small tree native to regions of Asia, the Mediterranean, and North Africa. Its scientific name is Nerium oleander, which belongs to the dogbane family (Apocynaceae).
The name “oleander” is believed to have originated from the ancient Greek words “Elia” and “Andros,” which mean “olive tree” and “man,” respectively. This is likely due to the similarity between the leaves of the two plants. Another theory suggests that the name comes from the Latin word “olea,” which means “oil,” referring to the oily nature of the plant’s leaves.
Oleander is known for its showy, fragrant flowers in shades of pink, white, red, and yellow. While it is a popular ornamental plant in many parts of the world, it is important to note that all parts contain toxic compounds, including oleandrin, which can be lethal if ingested. Therefore, caution should be used when handling or growing Oleander.
Although oleander flowers are undeniably beautiful and emit a sweet fragrance, it is important to recognize that they are highly poisonous.. Therefore, handling these flowers with caution and understanding how to care for oleanders appropriately is essential. Pay attention to care for Oleander plants properly to avoid severe health complications.
To maintain a healthy and thriving Oleander plant, it is necessary to follow certain guidelines. During autumn, reducing watering and applying a slow-release fertilizer are recommended to aid the plant’s growth. As winter approaches, it is vital to protect the plant from harsh weather conditions, such as frost, by keeping it covered. Furthermore, before the onset of new growth in late spring, it is recommended to remove any spent flowers and leaves to allow for healthy growth. By adhering to these guidelines, your Oleander plant can flourish while remaining safe and healthy for all.
How to Care for Oleanders
Proper care is essential to keep Oleander plants healthy and to thrive. Here are some tips for caring for Oleander:
- Light
Proper lighting is crucial for the growth and development of Oleander plants. During the winter months, it is essential to keep the plants out of direct sunlight, as too much exposure to the sun can cause damage to the leaves. In contrast, Oleander plants require plenty of bright light to thrive during the summer months. However, it’s important to avoid placing the pots directly beneath lights, which can cause scorching and leaf burn.
- Soil
The type of soil you use is also essential when growing Oleander. It is best to grow them in colder regions in pots filled with peat moss, perlite, and sand. This combination provides excellent drainage and helps to prevent waterlogging, which can cause root rot. A large container filled with peat moss and vermiculite will suffice in warmer regions. Place the container in a bright spot away from direct sunlight and keep the soil moist but not soggy.
- Watering
Oleander plants require consistent watering, but it’s important not to overwater them. Maintain soil moisture, but avoid waterlogging and letting it dry out entirely. It’s recommended to check the pots daily to ensure they are not drying out, and water as necessary.

- Fertilizing
Fertilizing your Oleander plants is crucial for healthy growth and blooming. Feed the plants a balanced fertilizer every two weeks during the growing season. If planting outside, use a slow-release fertilizer to provide nutrients to the plants over an extended period.
- Pruning
Prune your Oleander in the late winter or early spring before new growth begins. Remove dead, damaged, or diseased branches, and shape the plant as desired.
- Pests and diseases
Keep an eye out for common pests such as spider mites, scale insects, and mealybugs, and treat them promptly with insecticidal soap or neem oil. Oleander can also be susceptible to fungal diseases, so avoid overhead watering and provide good air circulation around the plant.
- Winter care
Protect your Oleander from frost by covering it with a blanket or moving it to a sheltered location during winter.
- Temperature and Humidity
Oleander plants thrive in temperatures between 15°C (59°F) and 25°C (77°F). If temperatures drop below ten °C (50°F), they may not survive. High humidity levels can also benefit Oleander plants, but they can still thrive in drier climates as long as they are watered regularly.
It’s also important to remember that all parts of the Oleander plant are toxic, so take care when handling it and keep it away from children and pets.
When To Prune Oleanders?
Oleander plants require proper pruning to keep them healthy and promote new growth. Here are some tips on when and how to prune Oleanders:
- Winter Pruning:
Prune Oleanders in late winter or early spring before new growth begins. Cut back the stems to three pairs of leaves, removing any dead or diseased wood. You can also remove any suckers that have grown around the base of the plant. This pruning will help to promote new growth and give the plant a more balanced shape.
- Spring Pruning:
After the last frost has passed in late spring, it’s time to do more pruning. Cut out all but one pair of leaves at ground level, as this will encourage the plant to produce new growth from the base. It’s also a good time to cut off flower stalks and remove any spent flowers to encourage more blooms.
- Autumn Pruning:
You can do more light pruning in early autumn to keep your Oleanders in good shape. Cut back the stems to two pairs of leaves, removing any dead or diseased wood. This will help to keep the plant from getting too leggy and promote more compact growth.
It’s essential to use sharp, clean pruning shears when pruning Oleanders, as this will help to prevent damage to the plant. Be sure to carefully dispose of any plant material, as all parts of the Oleander plant are toxic if ingested.
Pruning Oleander planted in the ground
Pruning Oleander plants planted in the ground requires a different approach than those grown in containers. Here are some additional tips to consider when pruning Oleanders that are planted in the ground:
- Timing
When pruning Oleanders planted in the ground, it’s important to do it at the right time to avoid damage to the plant. The ideal time to prune Oleanders planted in the ground is during late winter or early spring. This timing allows new growth to emerge in the spring and summer months.
- Tools
To prune Oleanders in the ground, you will need a pair of sharp pruning shears or loppers, depending on the size of the branches. Make sure to clean and disinfect your tools before and after pruning to prevent the spread of disease.
- Technique
When pruning Oleanders that are planted in the ground, start by removing any dead or diseased wood. Next, prune the branches back to a node or bud, leaving three to five leaves on each stem. Be sure to cut at a 45-degree angle to promote healing and prevent water from pooling on the cut surface.
- Shape
Cut back any long or overgrown branches to shape your Oleanders to promote more compact growth. It’s also essential to prune any suckers or branches growing from the base of the plant to keep it looking neat.
- Safety
It’s important to note that all parts of the Oleander plant are toxic if ingested. Please wear gloves and protective clothing when pruning, and carefully take care of any plant material.
Pruning Oleander planted in pots
Pruning Oleander plants that are grown in pots is a necessary step to maintain the health and shape of the plant. Here are some additional tips to consider when pruning Oleanders that are planted in pots:
- Timing
When pruning Oleanders planted in pots, it’s best to do it in late winter or early spring before new growth begins. This timing allows new growth to emerge in the spring and summer months.
- Tools
To prune Oleanders in pots, you will need a pair of sharp pruning shears or scissors, depending on the size of the branches. Make sure to clean and disinfect your tools before and after pruning to prevent the spread of disease.
- Technique
Start by removing any dead or diseased wood, cutting back to a healthy, live branch or stem. Next, prune the branches back to a node or bud, leaving three to five leaves on each stem. Be sure to cut at a 45-degree angle to promote healing and prevent water from pooling on the cut surface.
- Shape
Cut back any long or overgrown branches to shape your Oleanders to promote more compact growth. It’s also important to prune any suckers or branches growing from the base of the plant to keep it looking neat. Also, could you remove branches crossing or rubbing against each other to prevent damage?
- Size of Pot
It’s important to consider the size of the pot when pruning Oleanders. If the pot is too small, the plant may become root-bound, leading to poor growth and health. You may need to prune more heavily to keep the plant’s size manageable for its pot.
- Safety
Remember that all parts of the Oleander plant are toxic if ingested. When pruning, wear gloves and protective clothing, and dispose of any plant material carefully.
Pruning Oleander plants that are grown in pots is a crucial step in maintaining their health and shape. By pruning at the right time, using the proper tools and techniques, shaping the plant, and considering the size of the pot, you can keep your Oleanders looking beautiful and thriving for years to come.
How to Trim an Oleander
Trimming an Oleander is important in keeping it healthy and promoting new growth. Here are some steps to follow when trimming an Oleander:
- Timing: The best time to trim an Oleander is in late winter or early spring before new growth begins. Avoid trimming during hot weather or the fall when the plant prepares for winter.
- Tools: You will need a pair of sharp pruning shears or loppers, depending on the size of the branches you need to trim. It’s important to use sharp tools to make clean cuts that will heal well.
- Safety: All parts of the Oleander plant are toxic if ingested. Please wear gloves and protective clothing when trimming, and please make sure to take care of any plant material carefully.
- Remove dead or diseased wood: Start by removing any dead or diseased wood by cutting it back to a healthy, live branch or stem. Cut at a 45-degree angle to promote healing and prevent water from pooling on the cut surface.
- Cut back overgrown branches: Trim back any long or overgrown branches to promote more compact growth. It’s also important to prune any suckers or branches growing from the base of the plant to keep it looking neat.
- Remove spent flowers: Cut off the flower stalks and remove spent flowers to encourage new blooms.
- Shaping: To shape your Oleander, cut back branches crossing or rubbing against each other to prevent damage. You can also shape the plant by selectively trimming branches to encourage a specific growth pattern.
- Final touches: After trimming, water the plant well to help it recover from pruning stress.
Common Issues
Oleanders can also be prone to several common issues, including:
- Aphids: Aphids can harm oleanders by attacking the leaves and flowers. Using insecticidal soap or horticultural oil can help control these small insects.
- Scale insects: These pests are small, oval-shaped insects that attach themselves to the leaves and stems of oleanders. They can be treated with a systemic insecticide.
- Leaf spot: This fungal disease can cause yellow or brown spots on the leaves of oleanders. It can be controlled with fungicides or by removing infected leaves.
- Root rot: Overwatering or poor drainage can lead to root rot in oleanders, which can cause the leaves to turn yellow and wilt. To prevent root rot, it is important to ensure the soil is well-drained and to avoid overwatering.
- Chlorosis: Oleanders may develop chlorosis, where the leaves turn yellow due to a lack of chlorophyll. Nutrient deficiencies, such as a lack of iron or magnesium in the soil, can cause this. Chlorosis can be treated with fertilizers that contain the missing nutrients.
What we love from Amazon this week
Buy these wonderful flowers directly from Amazon: