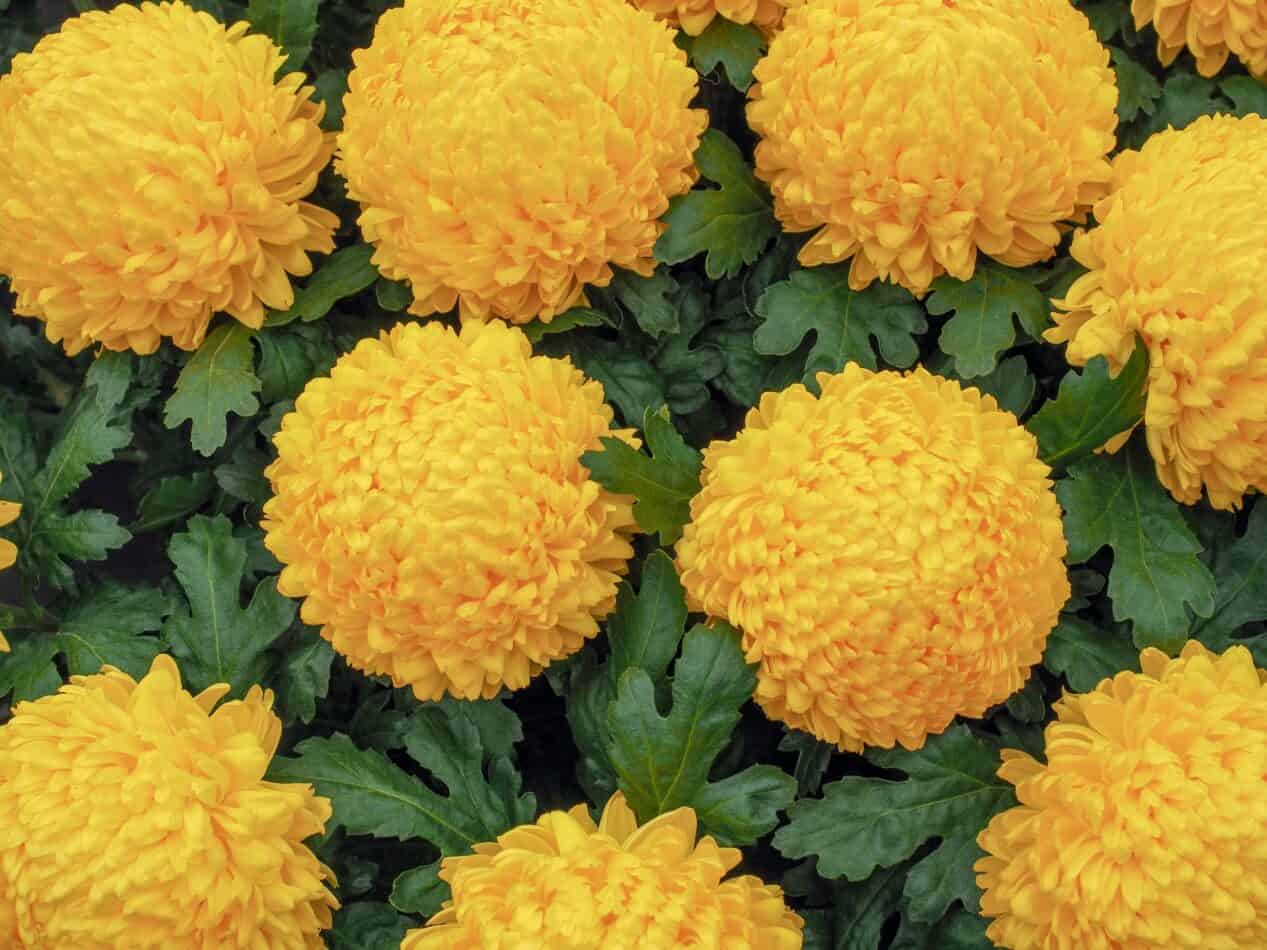
Groundcover roses are a diversifying shrub rose with glossy foliage and prickly stems. They bloom profusely with a variety of single or double blooms, possessing a delightful fragrance and a range of delicate shades. One of their key benefits is that they exhibit a resurgence of blooms over the course of a year — making them ideal for adorning sloping areas or banks. They are relatively easy to tend and resistant to most diseases, with “Flower Carpet Appleblossom,” “Sweet Drift,” and “Popcorn Drift” being prime examples of this species.
Etymology
Roses have been known to the ancient world since the dawn of civilization. Their use in poetry, literature, and art throughout the ages is testament to their personal and cultural importance. The Latin word for rose, rosa, likely stemmed from the Greek rhodon and the ancient Armenian humor, or hand-shaped flower motif, for the same. The descriptive value of the term groundcover rose refers to its have a wide-reaching, substrate embracing growth and cascading flora.
How To Plant
Groundcover Roses should be planted in well-drained soil, preferably in an area that receives full sun for most of the day for best performance. When planting, ensure the grafted root is at or slightly below the soil surface – this facilitates adequate moisture to the root system and creates an effective seal against severe weather. Moderate amounts of fertilizer should be applied at the time of planting and several more times throughout the growing season. When watering, recognize that overwatering can be detrimental and instead, target deep, infrequent doses of irrigation.
Meaning and Symbolism
Throughout history, roses have enjoyed a spectrum of symbolic significance that centers around themes of love, hope and admiration. Groundcover roses—and roses in general—are associated with beauty, new beginnings, and secret desires. Additionally, they are linked to the spiritual realm and their delicate petals can be used to represent the cycle of life, death, and rebirth.
History, Mythology, and Religious Significance
Roses have always been deemed to be special, and one of its earliest references appears in Greek mythology. Aphrodite—the goddess of love—surrounded herself with roses and was also thought to have been born from a rose blossom. It’s a motif which endures even to modern day as a representation of love, beauty, and the unfettered pleasure of beauty.
In the Christian tradition, roses are symbols of the resurrection – a show of faith and a personal reminder that beauty and hope will always persevere. Furthermore, in the context of different religions, roses have often been used to represent a reduced emphasis on ego and greater connection to a higher spiritual power.
Flower Varieties and Their Defining Characteristics
Groundcover roses come in a range of varieties and hues, exhibiting a wide variety of sizes, shapes and scents. Below are a few common varieties known for their bright and fragrant blooms:
- Popcorn Drift – A low-growing, white-coloured groundcover rose with light fragrant petals and bright yellow stamens. It is a tidy, round shrub is with flowering clusters of 4-7 blossoms. It is hardy to -25 degrees F and is moderate heat-tolerant.
- Sweet Dream – A spreading, vigorous shrub with fragrant, pink flowers that have yellow stamens in the centers. Its bushy growth makes it a good choice for low hedges, mass planting and erosion control.
- Flower Carpet Apple Blossom – Rounded mounds of foliage are covered by double blooms in pink with yellow stamens. This low maintenance rose is resistant to insects and disease and blooms late spring to mid-fall.
How to Pot and Repot
Groundcover roses can be planted in flower pots or planters – ready to be enjoyed indoors or out. When potting, use soil that is light and airy – potting soil amendment can be added. Repotting your Groundcover roses should be done sparingly and avoid too-frequent replanting as this can lead to root damage. If repotting is required, make sure to plan ahead – use a flower pot that is 5-6 inches larger in diameter than the current one, and be sure to water thoroughly before and after the transplant.
How to Prune
Pruning is a critical step in the cultivation of Groundcover Roses. Pruning helps to promote air circulation in the plant and encourages new flowering growth. It should be done in late winter to early spring, when the risk of cold snaps has passed and temperatures are above freezing. If a plant does not seem to be flowering or exhibiting signs of weak growth, pruning may be appropriate. To start, simply use pruning shears to cut off dead, diseased, and weak stems, adhering loosely to the shape of the bush. Removed canes should be discarded properly.
How to Propagate
Groundcover Rose propagation can be done either with seeds or with cuttings. To propagate with cuttings, select healthy leaves from healthy stems and dip the cut ends in a rooting hormone. Place the stems in a loose soil or a soil-less potting mix and water thoroughly. The new plant should begin to establish in a few weeks, provided the surrounding conditions are suited for growth.
Common Pests and Diseases
Groundcover roses are generally disease and pest-resistant, but particular diseases, such as black spot, powdery mildew, and rust, can affect the plants when the leaves remain wet for lengthy periods of time. Some insects, such as aphids and Japanese Beetles, may also feed on the foliage, though their effects are usually minimal.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q. How often should I water my Groundcover Roses?
A. Groundcover Roses require deep, infrequent watering. Generally, once per week should suffice with supplemental waterings during periods of drought.
Q. How do I prevent disease in my Groundcover Roses?
A. Proper care and sanitation is essential to preventing diseases in Groundcover Roses. Avoid over-watering and remove any diseased leaves and stems immediately. Pay careful attention to the pH of the soil too, as roses prefer slightly acidic conditions.
Q. When should I prune my Groundcover Roses?
A. Pruning should be done in late winter to early spring – generally between February and April.
Table Fact Sheet
| Groundcover Roses | Rosa |
|---|---|
| Family | Rosaceae |
| Plant Type | Shrub |
| Mature Size | 1–3 feet tall and 1–3 feet wide |
| Sun Exposure | Full sun preferably |
| Soil Type | Well-drained soil |
| Soil pH | Slightly acidic (pH 6.5) |
| Bloom Time | Late spring to mid-fall |
| Flower Color | Wide variety of colors |
| Hardiness Zones | 4–9 |
| Native Area | Various parts of the world |
What we love from Amazon this week
Buy these wonderful flowers directly from Amazon: