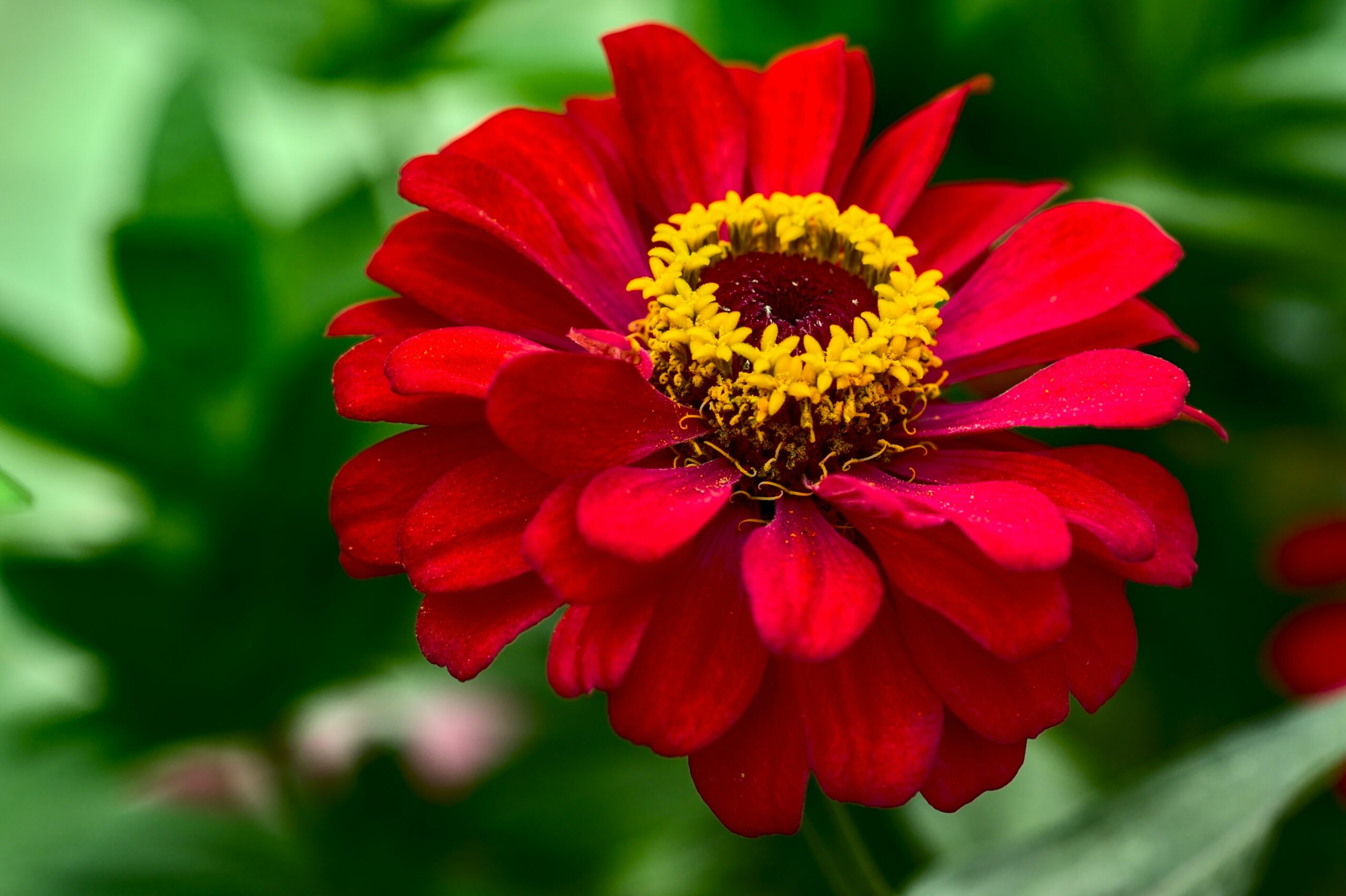
Zinnia is a beautiful flower that grows well indoors. They come in a wide variety of colors and patterns. Zinnias are perennial flowers that bloom throughout the summer months. The plant has a long history of being grown in gardens and landscapes worldwide.
Zinnias were named after James Edward Smith Zinn, who was a botanist at Harvard University. He discovered them growing wild along the banks of the Hudson River near New York City. Zinnias are members of the large Aster family and are closely associated with dandelions. They are primarily a North American species, but there are some forms of wild zinnias growing in Central America. Learning how to grow and care for zinnias is easy and simple. We highlight few simple steps to master how to grow zinnias quickly.

How to Grow and Care for Zinnias
- When to plant
Zinnias can be planted in spring or summer. They do best when temperatures are between 60°F and 80°F during the day and 50°F at night.
- Location
Zinnias grow best in well-drained soils rich in organic matter. They prefer full sun but tolerate some shade. Plant in groups or mounds for better air circulation.
- Planting Method
Dig twice as wide as the root ball and three times as deep. Set the plant on its side in the center of the hole. Fill around the roots with topsoil, tamping it down firmly. Water thoroughly and wait until new leaves appear before watering again.
How to Grow Zinnia Plants
- Plant in groups or mounding rows. Please remember that a single zinnia plant can produce up to 100 blooms. For maximum bloom production, deadhead your zinnias frequently.
- Zinnias are drought tolerant and thrive in dry conditions. In humid climates, mulch around your zinnias with straw or leaves to conserve moisture.
- You may need to repot your zinnias twice a year.
- The foliage of zinnias turns yellow in autumn. Cut back all but the newest growth before winter arrives. Prune away damaged parts of the plant.
- Zinnias should not be overwatered because this encourages disease problems.
- Avoid using a fertilizer that contains nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, or sulfur. These nutrients promote root rot.
- To prevent pests, apply insecticidal soap or horticultural oil.
- Zinnias require regular watering to maintain good health.

Ideal Conditions for Growth
Zinnias grow best in well-drained soils rich in organic matter and learn how to grow and care for zinnias is easy. They don’t like too much water, but they appreciate some humidity during the summer months.
In the garden, zinnias prefer cooler temperatures than most plants. In warmer climates, they may require protection from the hot afternoon sun.
- Light
Zinnias have no special requirements regarding light. They grow best in full sun, though they can tolerate partial shade.
- Soil
Zinnias prefer loamy, well-drained soil rich in organic matter. Potting mix made from equal parts peat moss and sphagnum moss works well.
- Water
Zinnias do not need a lot of water; they thrive in drier conditions. However, if you live in an area where summers are humid, you may find that your zinnias need supplemental irrigation.
- Fertilizer
The best fertilizer for zinnias is compost tea. Compost tea is made by adding leaves, grass clippings, and manure to water and letting it sit for several days. This mixture encourages beneficial bacteria to grow and break down plant nutrients.
- Pruning
You can prune zinnias as needed to keep them looking neat and attractive. Remove any dead or diseased branches, then cut back new growth to about 6 inches above ground level.
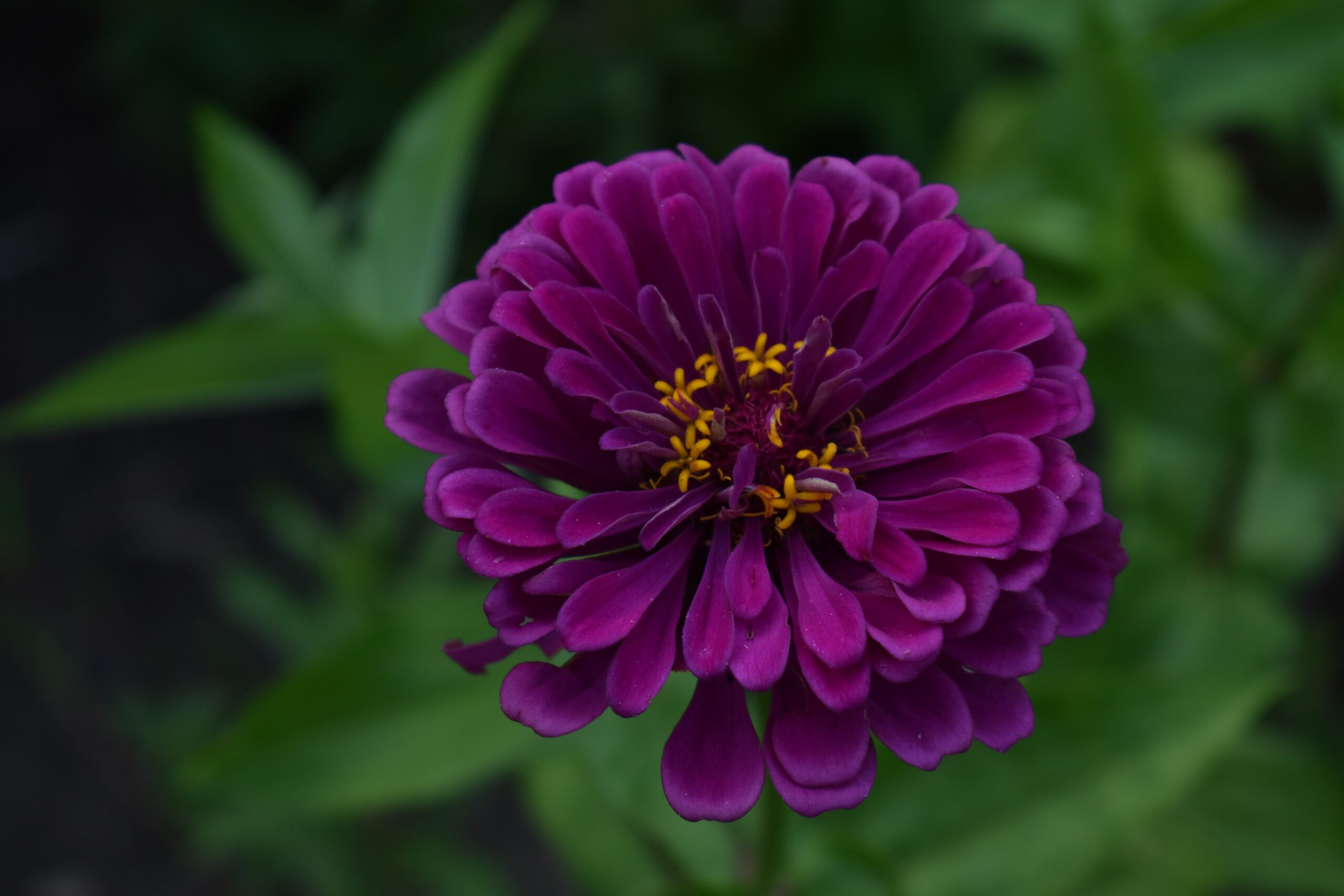

Zinnia Varieties
There are many gorgeous varieties to choose from, with new ones being introduced to the market each year. The best varieties for growing zinnias include ‘Candy Cane,’ ‘Fiesta,’ ‘Jubilee,’ ‘Pixie,’ ‘Sunburst,’ ‘Tangerine Dream,’ and ‘White Swan.’
Propagating Zinnias
To propagate zinnias:
- Take stem cuttings in late spring or early summer.
- Gently tease apart the leaf nodes on the cutting to expose the bud.
- Place the tip of the cutting into moist sand or vermiculite.
- Keep the container in a warm place until the cutting has rooted.
- Transplant the seedlings outdoors once the danger of frost has passed.
Pests and Diseases
Zinnias are relatively pest-free, although aphids sometimes feed on the underside of leaves. Spray plants with insecticidal soap when you see signs of infestation.
If you notice brown spots on leaves, suspect fungal infection. Wash infected areas with a solution of 1 tablespoon baking soda per quart of water. Repeat this procedure every few weeks until symptoms disappear.
If you see small holes in leaves, suspect whitefly. These tiny insects suck the sap out of plants, causing leaves to dry up and drop. Use a spray bottle to mist plants with horticultural oil.
Diseases such as mildew, anthracnose, and powdery mildew can cause foliage damage. To prevent these diseases, ensure your plants get plenty of sunlight and air circulation.
Insect pests include thrips, aphids, spider mites, mealybugs, and whiteflies. You can control most pests using organic sprays, traps, or pheromone-based products.
What we love from Amazon this week
Buy these wonderful flowers directly from Amazon: