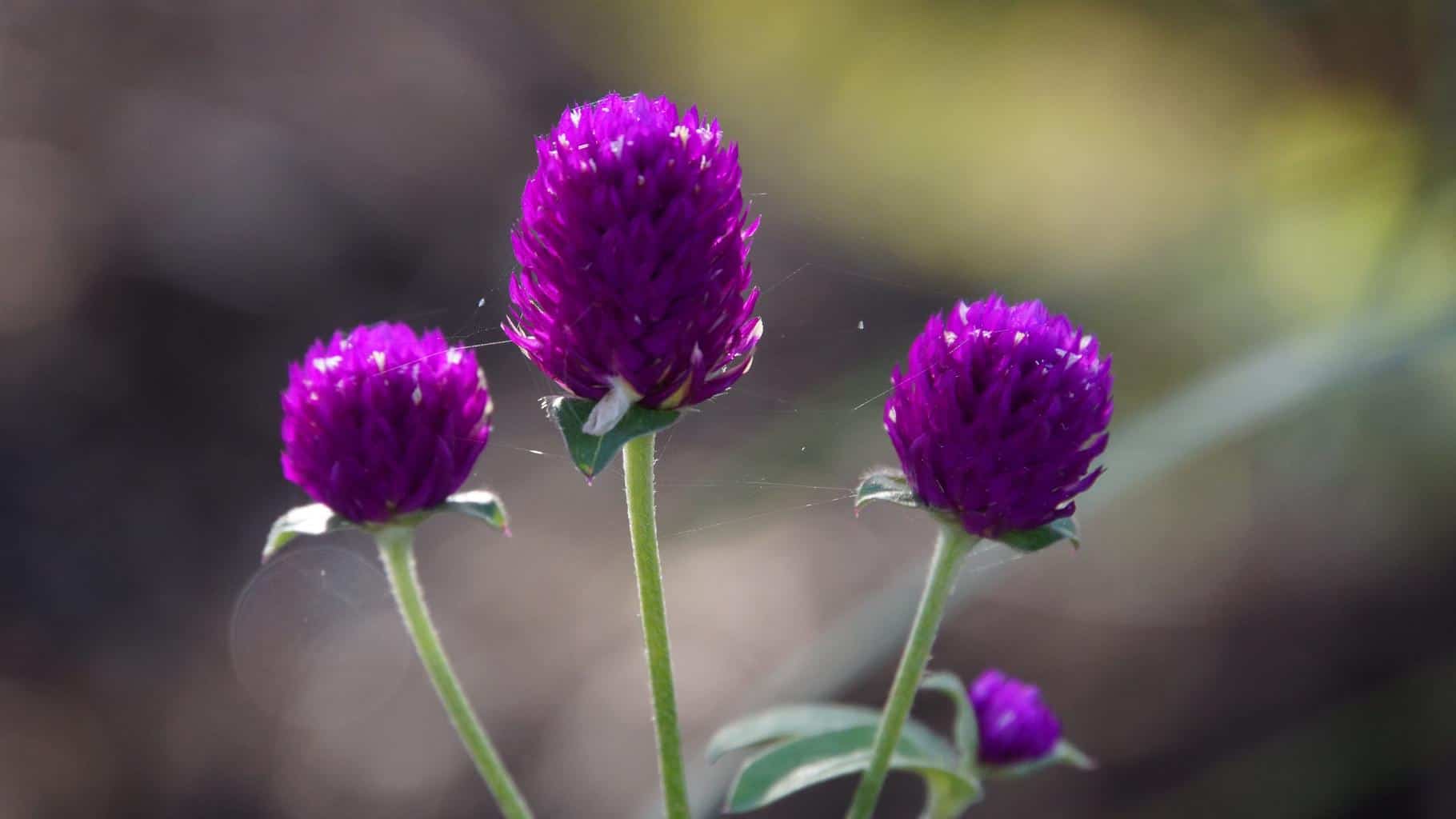
The Bearded Irises, also known as Iris germanica, are a genus of flowering plants native to Europe and North America. They belong to the family Iridaceae, commonly referred to as the iris family. The term “iridaceae” is derived from the Latin word ‘iris’ which means rainbow. This moniker pays homage to the plant’s ability to produce many different varieties of flowers in a brilliant array of colors. These eye-catching blooms are highly sought after and have become a popular garden addition in recent years.
Etymology
The genus name ‘Iris’ comes from Greek mythology, the goddess ‘Iris’ was the messenger of the gods. The specific epithet germanica translates to “of Germany”, alluding to the presumed country of origin. Andromeda, the goddess of Ethiopia, was depicted wearing an iris across her breast, henceforth making the term “iris” synonymous with loyalty.
How to Plant and Grow Bearded Irises
Bearded Irises prefer full sun, with 4–6 hours of direct sunlight per day, and they are quite hardy and can tolerate a range of soil types, including clay and sandy soil. When planting, make sure to give the Iris proper drainage by planting in raised beds or raised containers. If there is not proper drainage, the rhizomes may rot. The ideal soil pH range is 6.1 to 7.5. Moreover, these plants are very drought and heat tolerant and do not require frequent watering, however, they do benefit from soil that’s moist but not soggy. Fertilizer should be applied during the growing season, but not when the plant is entering dormancy.
Meaning and Symbolism
The iris is known worldwide as a symbol of faith, hope, and wisdom. For Christians, it symbolizes purity and is linked to Mary and the Virgin Mary. To the ancient Greeks, the flowers symbolized immortality, and to the French it is a sign of hope and valor. In Japan, iris flowers signify courage and faithfulness. To many, the Bearded Irises are a symbol of promise and courage in their journey through life.
History, Mythology and Religious Significance
In antiquity, the Greeks and Romans reverenced the Iris as a Sacred Flower of Juno and Iris, the goddess of the rainbow. During the Middle Ages, the Iris was a symbol of the Virgin Mary, representing purity and faith. It was believed to have the power of warding off evil spirits, and was also thought to be a sign of hope and a reminder of the miracles that occur on earth. In the Christian faith, the Bearded Iris is linked to the Virgin Mary, the Lily of the Valley, and Mary Magdalene. In the Western world, the iris is given as a coronation gift to the newly crowned Kings and Queens of England.
Flower Varieties and Their Defining Characteristics
Bearded Irises come in a variety of lovely flower colors, including shades of purple, yellow, white, and blue. Some varieties are scented and have striking markings, such as stripes, spots, and veining. These flowers usually grow in clumps and range in height from 45 cm (18 in) up to 90 cm (35 in) tall. All blooms produce three upright petals and three dropping petals, with a beard in the center to guide the pollinators and frilled edges. Most Bearded Irises bloom from spring, and some rebloom in the summer and fall.
How to Pot and Repot Bearded Irises
When potting Bearded Irises, select a container with good drainage holes and use a balanced, low-nitrogen blend of fertilizer. Irises prefer less water and a moderate amount of fertilizer. To repot, use a clean container with a layer of pebbles or gravel at the bottom and fill it with a fast-draining, well-aerating soil. Make sure to keep the rhizomes above the soil line, as well as trim off any dead leaves and old foliage. Irrigate well after planting and keep the plants moist, but not waterlogged. After the foliage appears and flowers blooming, use a balanced fertilizer twice a month.
How to Prune
Bearded Irises need to be pruned to keep their shape and encourage healthy growth. Prune the plants in late spring, when the leaves emerge. Remove any dead foliage to eliminate sources of disease transmission and cut back the stalks after flowering. Pruning is beneficial for the plant’s root system and helps to keep the plant healthy and vigorous. Prune away any broken, weak or dead blooms, and use sharp scissors and shears to avoid damaging the foliage. Deadheading is also recommended to encourage the plant to rebloom after it has flowered.
How to Propagate Bearded Irises
Propagation is most easily done through division, which involves breaking up larger clumps into smaller ones. Ideally, the rhizomes should be divided in the spring, after flowering has finished and as soon as new growth has emerged, or in the fall or winter. If a clump has become too large or you want to share with a friend, cut the rhizomes lengthwise or in small pieces with a sharp, sterile cutting tool. Make sure to remove any old dead foliage or stems and discard and pot the pieces straight away in new, well-aerated soil. Water the newly potted plants well and keep moist over the summer months.
Common Pests and Diseases
Bearded Irises are prone to aphids, leafhoppers, thrips, spider mites and various caterpillars. To prevent pests from attacking, be sure to check plants regularly – leaf and foliage should be visibly inspected for any signs of infestation. Additionally, don’t overcrowd the plant and ensure it is kept in a well-ventilated area where sunlight can reach it. Diseases that may occur in Iris germanica include anthracnose, a fungal disease that can cause blight and infect foliage, and crown and root rot, which can cause the plant’s rhizomes to turn mushy and decay.
Frequently Asked Questions about Bearded Irises:
Q. How can I encourage Bearded Irises to rebloom after flowering?
A. To encourage reblooming, deadhead the flower stalks as soon as they have finished flowering, and provide plenty of water and fertilizer. Additionally, some varieties of Iris germanica are prone to reblooming in fall, so be sure to check labels if you are looking for a fall blooming variety.
Q. Are Bearded Irises suitable for container gardening?
A. Yes, Bearded Irises are suitable for both indoor and outdoor container gardening. They prefer full sun and fast-draining soil, so make sure to choose a pot with plenty of drainage holes and fill it with a balanced, nutrient-rich soil. Additionally, make sure to water regularly and keep the soil moist, but not waterlogged.
Q. What is the difference between Bearded Irises and other Iris varieties?
A. The Bearded Irises have greater variance in color and more prominent beards compared to other varieties of Irises. Furthermore, the Bearded Irises are more hardy and some varieties may even rebloom in the fall.
Fact Sheet
| Flower | Bearded Irises |
| Scientific Name | Iris germanica |
| Family | Iridaceae |
| Plant Type | Perennials |
| Mature Size | 45 cm (18 in) to 90 cm (35 in) |
| Sun Exposure | Full sun |
| Soil Type | Well-draining |
| Soil pH | 6.1 to 7.5 |
| Bloom Time | Spring/summer/fall |
| Flower Color | Purple, yellow, white, and blue |
| Hardiness Zones | 3–10 |
| Native Area | Europe and North America |
What we love from Amazon this week
Buy these wonderful flowers directly from Amazon: