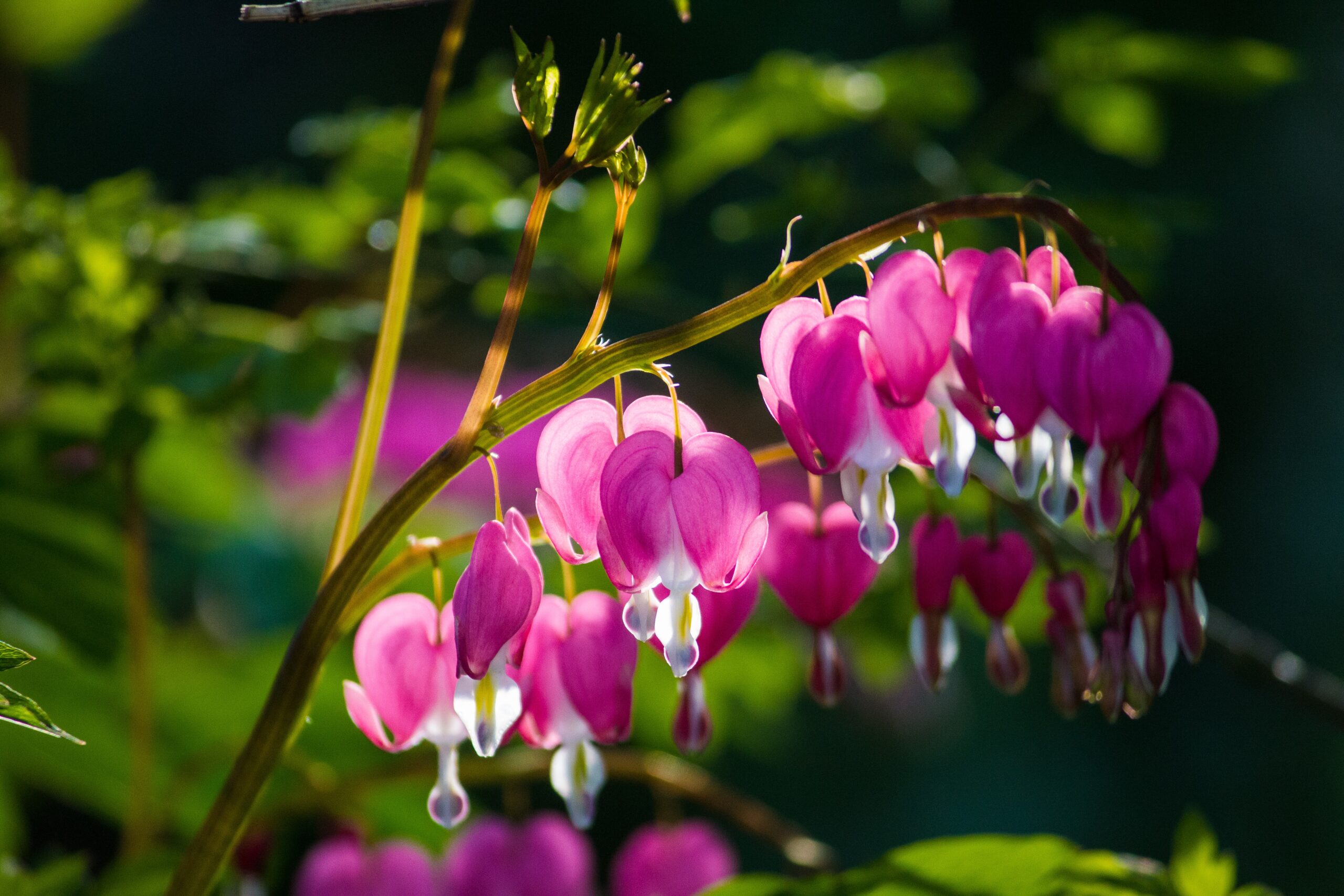
What’s a Bleeding Heart? No, we are not talking about a heartbroken teenager or a hopeless romantic!
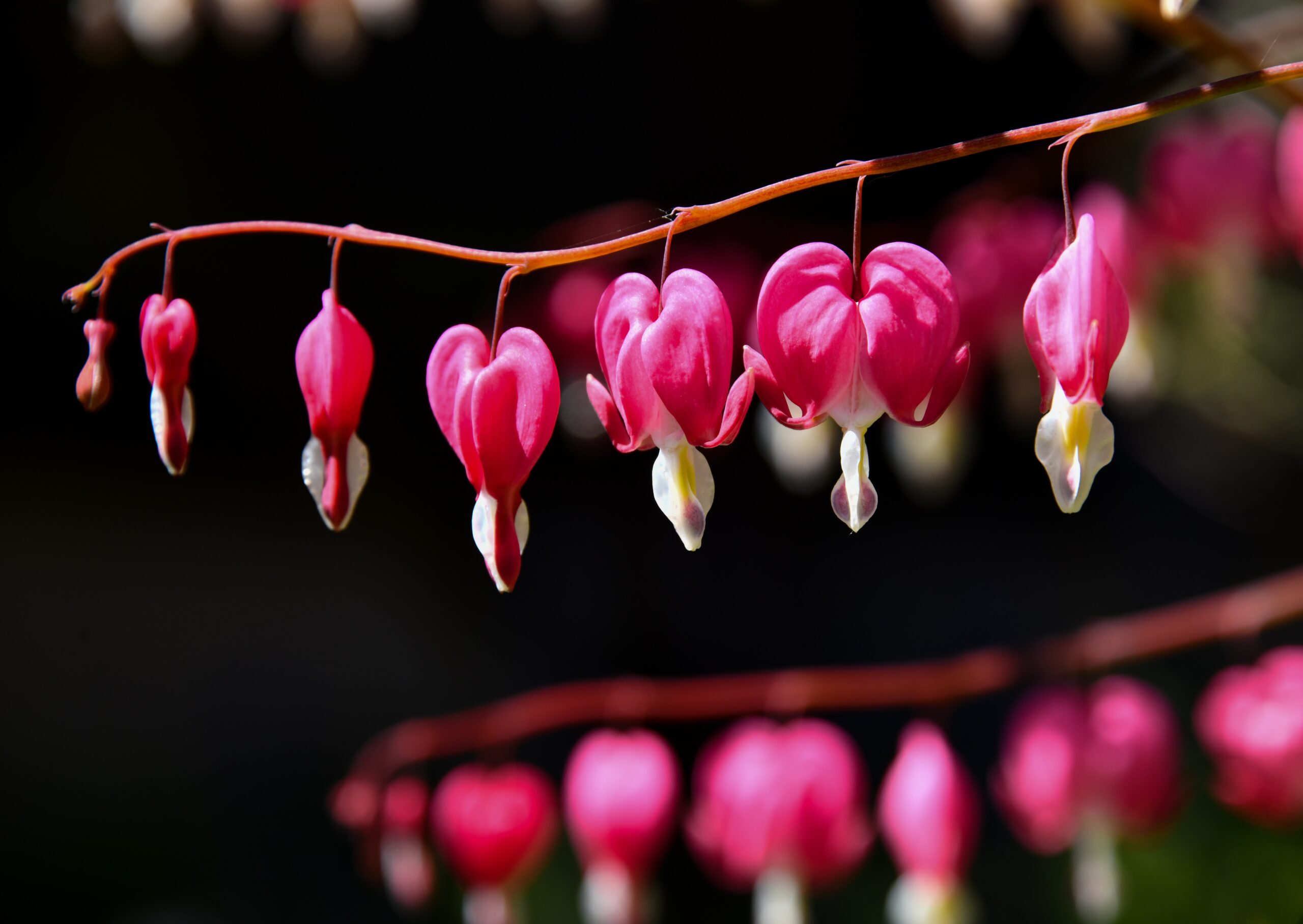
A Bleeding Heart, also known as Lamprocapnos spectabilis or Dicentra spectabilis, is a herbaceous perennial plant native to Asia. It is known for its unique and striking heart-shaped flowers, which typically bloom in late spring or early summer.
The Bleeding Heart’s flowers hang down from arching stems and feature distinctive pink or white heart-shaped petals with a droplet-shaped protrusion at the bottom, resembling a bleeding heart. The flowers are usually around 1 inch long and bloom in clusters on stems that can reach up to 3 feet in height.
It is also a popular ornamental plant in gardens and landscaping due to its beautiful and unique appearance.
However, let’s not forget that it is also toxic if ingested and can cause skin irritation, so it should be handled with care. The flowers are usually pink or white but come in other colors too. They look great in bouquets, and some even have edible petals.
So, what do we need to know to plant a bleeding heart and make it thrive? First of all, I would focus on the symbolism of this intriguing plant.

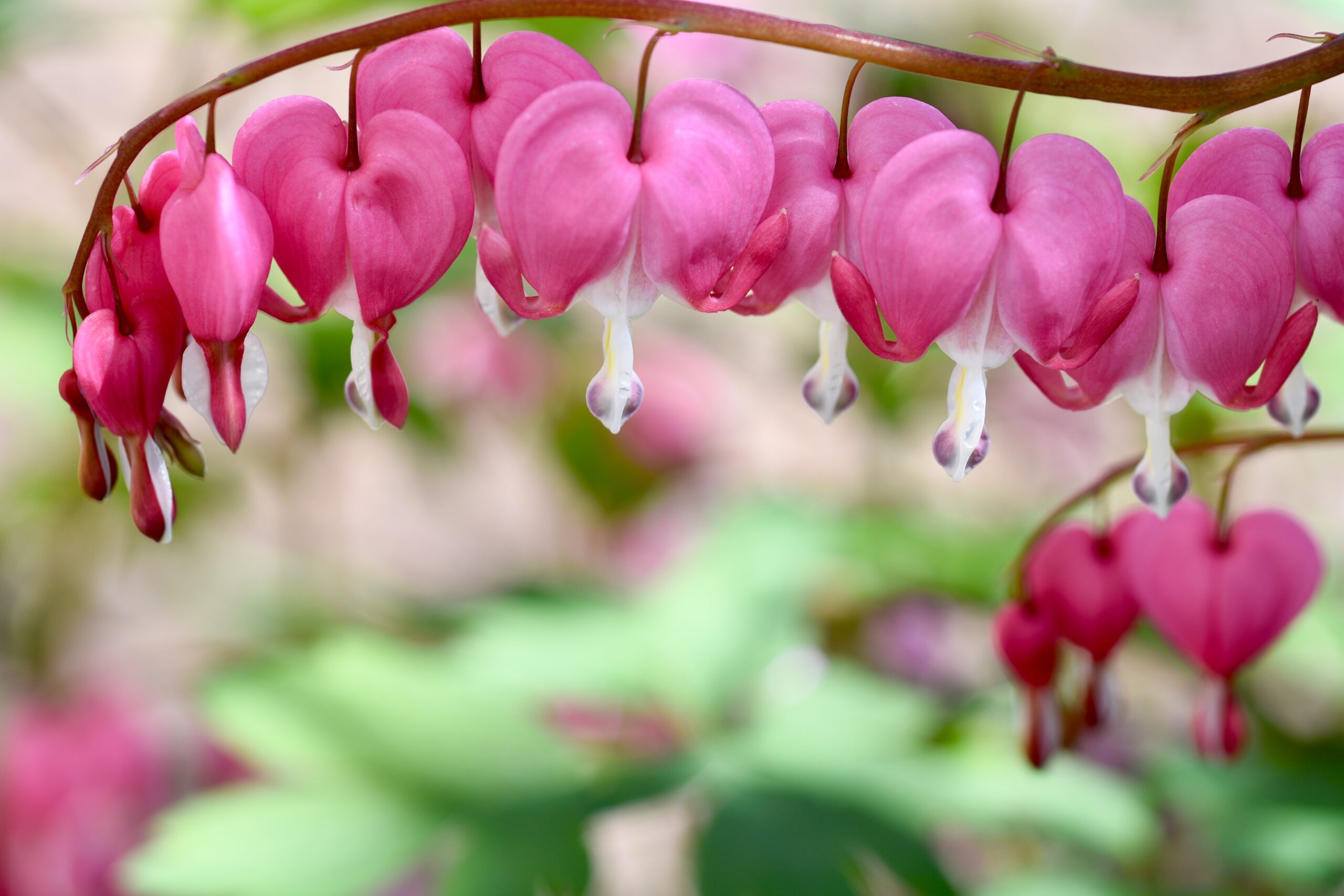
Meaning & Symbolism
Bleeding Heart plants have been associated with various meanings and symbolisms throughout history and in different cultures. Here are a few common interpretations:
-
Love and Romance:
In many cultures, the Bleeding Heart flower symbolizes love and romance, especially unrequited love. The heart-shaped flowers with a droplet-shaped protrusion at the bottom are said to represent a broken heart, which is bleeding and in pain due to unrequited love.
-
Compassion and Empathy:
The Bleeding Heart flower is also associated with compassion and empathy, due to its striking appearance and the emotional response it can evoke. Some people believe that growing Bleeding Heart plants can help foster these qualities in the gardener or observer.
-
Renewal and Rebirth:
In some cultures, the Bleeding Heart plant is associated with springtime and the renewal of life after winter. Its emergence from the soil and subsequent blooming are seen as symbols of rebirth and new beginnings.
-
Spiritual and Metaphysical:
In some spiritual and metaphysical practices, the Bleeding Heart plant is associated with the heart chakra, which is believed to be the center of love, compassion, and healing energy in the body. The plant is said to help balance and activate this chakra, promoting emotional healing and spiritual growth.
How to Grow Bleeding Hearts
The best way to grow bleeding hearts is to sow them directly into the garden in springtime. Sow seeds 1/4 inch deep and covers them lightly with soil. Keep the soil moist at all times. They like cool temperatures, so don’t plant them during hot weather.
If you’d instead start any bleeding heart plants inside, you can buy potted plants at nurseries or online retailers. Ensure choosing a container that allows drainage since the bleeding heart needs to stay wet to thrive.
Once your bleeding heart seedlings sprout, give them bright light and ample space to grow. You can either place them in a large window or move them outside under natural sunlight.
Once the plants reach 6 inches tall, you can begin fertilizing them regularly. Fertilize once per month with a slow-release fertilizer. Apply a small fertilizer to the soil around the plants’ crowns.
As the plants mature, they will produce more blooms. To maintain healthy buds, deadhead spent blossoms regularly. Remove any flowers that have turned brown or yellow.
When shall I plant it?
The best time to plant is between April and June when temperatures are warm enough to encourage germination without causing damage from frost. If you live in a cold climate, wait until late summer, after the last frost date has passed.
Growing conditions
Bleeding heart likes full sun and plenty of moisture. It’s hardy and drought-tolerant, so it won’t mind being planted in areas where there isn’t always water nearby.

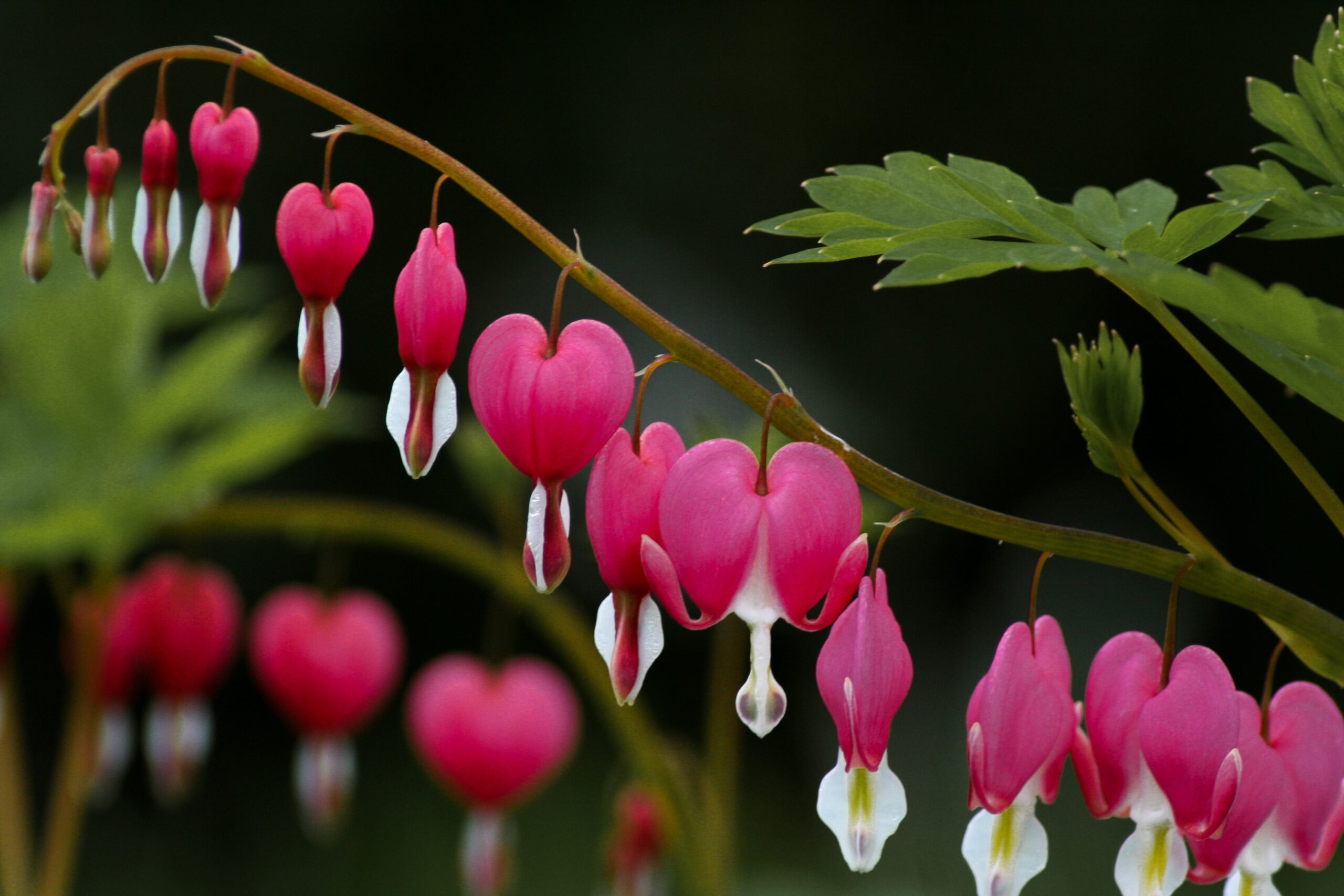
How to Plant it
Dig a hole twice as wide as the root ball and deep enough to accommodate the root system. Place the roots in the center of the hole and fill around them with potting mix. Water thoroughly and keep an eye on the plants during the first few weeks while they establish themselves.
After several months, you may notice new growth emerging at the base of the stems. This is your first sign that the plant is ready to be divided into individual plants.
Divide the clump by carefully cutting off the top third of each stem. Make sure to cut just above a node (the point where two leaves meet). Then gently tease apart the leaves until they separate easily. When you’re done dividing, replant the pieces in their holes.
Caring for your Plant
The most common problem with bleeding hearts is that they don’t like transplanting. If you move them from one location to another, keep them watered and fertilized, and give them plenty of room to grow, they should thrive.
Light
The bleeding heart loves bright light, but it does need some shade to protect its delicate foliage. In the heat of summer, you might want to provide additional shade to prevent scorching.
Soil
Bleeding heart requires rich, well-drained soil. Soak the roots before planting to help avoid transplant shock.
Water
Keep the soil evenly moist throughout the growing season. Too little water will cause the leaves to turn yellow and drop. Overwatering can lead to rot.
Temperature and Humidity
Bleeding heart needs average daytime temperatures of 70 degrees Fahrenheit and nighttime temperatures below 60 degrees Fahrenheit. The ideal humidity level is 50 percent.

Fertilizer
Feed the plants every three weeks with a balanced fertilizer. Use half the recommended rate for spring, then double the dose for fall.
Bloom Time
Bleeding hearts bloom all year long, but they tend to peak in early May.
Pruning
If you have many bleeding heart plants, you’ll probably want to prune them back once they start flowering. Remove any dead flowers or branches, especially those near the bottom of the plant. Also, remove any damaged or diseased parts.
Once the blooms fade away, trim back the remaining flower stalks to encourage bushy growth.
Propagating
The easiest way to propagate bleeding heart is from seed. Sow seeds indoors in late spring or early summer, then transplant them outside after all danger of frost has passed. Seeds should be sown at a depth of 1 inch. Germination takes 4 to 6 weeks.
Overwintering
To overwinter bleeding heart, dig up the plants when the ground begins to freeze. Please keep them in a cool greenhouse or garage until spring. You can also sow the seeds directly outdoors in the fall.
What we love from Amazon this week
Buy these wonderful flowers directly from Amazon: